- Joined
- Dec 14, 2010
- Messages
- 315
- Points
- 0
I think in every forum, there's an element of "We've answered that question 100 times already" but there's also equally as infrequently a compounded list that doesn't just say what something is, but explains what it is.
I've been browsing through the forum, and there's a few new people who ask similar questions over and over and I wanted to take some time and try and put everything together into the same space. Not so much a FAQ, but more of a bunch of laser terms (not acronyms) that get tossed around that someone who hasn't done the research themselves would know.
For a list of Abbreviations/Acronyms, please go to this awesome thread:
http://laserpointerforums.com/f44/acronyms-forum-42167.html
My thinking was that instead of simply answering the same 10 questions in 25 different new threads, we could just point the person here instead. Let them find out on their own. It's easy enough to say "go Google it" but sometimes it's not that easy. (Though in most cases it is) But people often want a simple, human explanation instead of a crazy technical answer that requires what seems like a PH.D in physics ;-)
So, that being said, I've put together a list of laser-related terms that get tossed around with the assumption that everyone knows what it means... And as a noob to lasers you might just find it a little overwhelming.
(Please feel free to add and correct terms that I've put in here, to make it more comprehensive. I'm not a laser genius, so I might mess up some of the terms or misunderstand... so this is a good opportunity for clarification too)
(Also, this is aimed at general DPSS/Diode lasers... I don't know a lot about gas lasers so any additional information that could be tossed in here would be fantastic. I just 'assume' that most newer folks interested in lasers nowadays typically start with DPSS or Diode lasers)
Arctic Silver
This is a thermal compound (see Thermal Paste) made by Arctic Silver Incorporated, used for conducting heat between two surfaces.
See Arctic Silver - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Collimated Light
Collimated light is light whose rays are nearly parallel. When light is said to be focused at infinity, what they're referring to is that the laser beam itself shouldn't expand for infinity. Collimation is referred in many aspects, from flashlights, to telescopes.
See Collimated light - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Diode
In electrical terms, a diode is nothing more than a 1-way cat-door. It will let electricity flow in one direction, but not another. When talking about lasers, the same is true, however there's a unique output of a laser diode. Between two metallic surfaces is a semi-conductor that will output collimated light, or light who's rays are nearly parallel, and similar in wavelength.

See Laser diode - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Diode Pumped Solid State
Diode Pumped Solid State, or DPSS for short, is a way of getting stimulated emissions of radiation, through a conversion process. "Typical" red diode lasers will output 660nm of light directly from the diode as collimated light. With a DPSS laser, there are crystals that are "pumped" by a diode that doesn't have the same frequency as the outgoing light.

This is an example of where green lasers typically get their output from.
There's an 808nm pump diode, who's purpose is simply to push 808nm laser light into a Nd:YVO4 or Nd:YAG crystal which produces laser light at 1064nm.
In turn, directly after that, is another crystal (KTP) which is a frequency doubler, and will effectively double the frequency from 1064 to 532nm which is the green light we see at the out-put end of lasers.
See Diode-pumped solid-state laser - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Divergence
Divergence is a measure of how much a beam will spread over time. A lower divergence means that a laser will maintain it's "beam" longer, where a higher divergence will spread out more. This isn't to be confused with focus however. A laser that is focused to infinity will still have divergence.
To calculate divergence, please see pseudonomen137's mRad calculator here:
pseudonomen137's JScript mRad Calculator
See Beam divergence - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Driver
A Driver in laser terms is a circuit board that is designed to provide a laser diode with a filtered/consistent amount of power. Similar to a driver circuit, however is typically a series of resistors, circuits and other elements that convert raw output from a battery to a steady flow of electricity the diode can handle.
See Sam's Laser FAQ - Diode Laser Power Supplies for more information.
Flexdrive
A Flexdrive is a driver (see above) model, and is a trademarked design for specific electronic circuit by DrLava:
Micro Flex Drive
Adjustable or fixed drivers are reffered to as their type. (Fixed driver outputs a fixed mAh, adjustable can be changed)
Host
In laser terms, a host is simply the shell or casing/housing of a laser diode+driver+battery assembly. There are several styles of host that exist, from pen hosts, to torch hosts.
Infrared
Infrared is simply light that exists outside of the visible spectrum for our human eyes. It's been broken up into 3 categories:
IR-A: 700 nm–1400 nm
IR-B: 1400 nm-3000nm
IR-C: 3000 nm-1mm
Typically handheld/Diode lasers will be between 700nm and 1000nm, 980nm and 808nm being pretty common. 808nm is also the diode used for powering green lasers.
See Infrared - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
IR Filter
IR Filter, or Infrared filter is a filter that has been designed to block infrared frequencies. This is common in green lasers, because of the 808nm and 1064nm light that is produced in the conversion process into 532nm. It's also often noted that a lot of cheaper "Chinese lasers" are missing these, causing them to potentially be more dangerous.
See Infrared cut-off filter - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
KTP Crystals- Potassium Trihydrogen Phosphate This material is a nonlinear optical material which is used in the frequency doubling stage of DPSS green lasers, and is the final stage of the conversion process into 532nm wavelengths.
See Potassium titanyl phosphate - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Milliwatt (mw)
Milliwatt, or mw for short, is a measure of output of electricity, where one milliwatt is equal to one thousandth of a watt.
<5 mw lasers are referred to as the 'safe lasers' because the BAR (Blink Aversion Reflex) is fast enough to prevent damage to the retina, according to the FDA.
See Watt - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information on watts, and
See Corneal reflex - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information on Corneal or aversion reflex.
Module
With reference to a laser module, this is a component usually includes the diode housing, driver, KTP and YAG crystals in the case of a DPSS Green laser, collimating lens, widening lens, etc.

This is an example of what a laser module looks like.
Often for DIY or Do-it-yourself projects, these modules will be purchased separately from a host, for users who wish to customize their laser assemblies.
mRad
mRad stands for milliRad which is a unit of angular measurement. Usually used in the context of divergence, it's a way of measuring or describing how much a beam will spread out over time.
See: Radian - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Multifunction
Multifunction lasers are lasers that serve multiple functions. Such as being a laser and a flashlight.
Over-spec
Over-spec is shortened for "Over Specification". When purchasing a laser, the laser is going to be "spec'd" or given specifications, usually referring to the wattage or milliwatts. A laser which performs with a higher output compared to the listed specifications is often refereed to as being over-spec.
Pointer
A pointer, not to be confused for a torch, is usually referencing it's host, or intended meaning. The terms seem to be interchangeable.
See Laser pointer - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Pump
Pump refers to the role a diode plays in a DPSS laser. The pump is simply the source which goes through a conversion process before being released as a final product.
Alternatively, laser pumping is the act of transferring energy from an external source into the gain medium of a laser. (The element that lases)
See Laser pumping - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
TEM (Hermite-Gaussian Modes)
This refers to the output of the laser and "how it looks". Sometimes mode jumping occurs with lasers, and that's honestly all I know about it.
What I can tell you is that there's a little diagram that shows you what the different TEM's look like:

See Gaussian beam - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Thermal Paste
This is a paste that separates spaces between two surfaces, and helps conduct heat. If you look at a heat syncs surface and another surface that the heatsink sits on, there's usually microscopic gaps because the surfaces aren't actually flat.

This is an exaggerated view, however does represent what microscopic imperfections could/do look like.
By filling the "TIM" whitespace, you're allowing more heat to be conducted between the two surfaces. In this example, it's talking about a heatsink and CPU, but in laser terms it is typically the diode housing and the host or heatsink.
Torch
This is in reference to the type of host, as well as it's role. Torches are not typically "pointers" in that they're not often used for pointing at objects, though they have been known to be used for such activities.

This is an example of a host that is a torch style.
Under-spec
Opposite of Over-spec. Short for Under Specification.
Wavelength
Wavelength is the length at which a waves shape repeats.
To humans, different electromagnetic wavelengths represent different colors, and serve different functions.

This is an example of the electromagnetic spectrum, which includes the visual spectrum of what humans can see/perceive with their eyes.
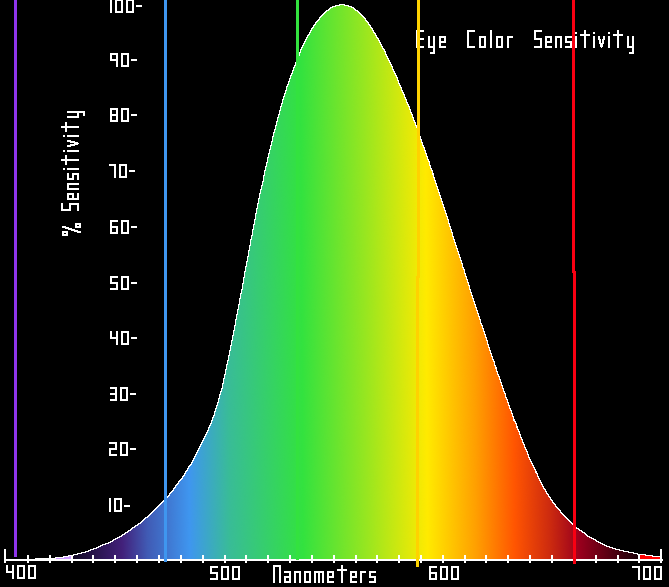
This is a chart showing the frequency response most sensitive to humans. Notice that green is the most sensitive, meaning it'll be the "most bright"
See Wavelength - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
YAG-Yttrium Aluminum Garnet
Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (YAG for short) is a synthetic crystalline material used in solid-state lasers, and can be doped into YAG to create Nd:YAG lasers.
This is also the first stage of transformation in DPSS Green lasers.
See Yttrium aluminium garnet - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
I've been browsing through the forum, and there's a few new people who ask similar questions over and over and I wanted to take some time and try and put everything together into the same space. Not so much a FAQ, but more of a bunch of laser terms (not acronyms) that get tossed around that someone who hasn't done the research themselves would know.
For a list of Abbreviations/Acronyms, please go to this awesome thread:
http://laserpointerforums.com/f44/acronyms-forum-42167.html
My thinking was that instead of simply answering the same 10 questions in 25 different new threads, we could just point the person here instead. Let them find out on their own. It's easy enough to say "go Google it" but sometimes it's not that easy. (Though in most cases it is) But people often want a simple, human explanation instead of a crazy technical answer that requires what seems like a PH.D in physics ;-)
So, that being said, I've put together a list of laser-related terms that get tossed around with the assumption that everyone knows what it means... And as a noob to lasers you might just find it a little overwhelming.
(Please feel free to add and correct terms that I've put in here, to make it more comprehensive. I'm not a laser genius, so I might mess up some of the terms or misunderstand... so this is a good opportunity for clarification too)
(Also, this is aimed at general DPSS/Diode lasers... I don't know a lot about gas lasers so any additional information that could be tossed in here would be fantastic. I just 'assume' that most newer folks interested in lasers nowadays typically start with DPSS or Diode lasers)
Arctic Silver
This is a thermal compound (see Thermal Paste) made by Arctic Silver Incorporated, used for conducting heat between two surfaces.
See Arctic Silver - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Collimated Light
Collimated light is light whose rays are nearly parallel. When light is said to be focused at infinity, what they're referring to is that the laser beam itself shouldn't expand for infinity. Collimation is referred in many aspects, from flashlights, to telescopes.
See Collimated light - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Diode
In electrical terms, a diode is nothing more than a 1-way cat-door. It will let electricity flow in one direction, but not another. When talking about lasers, the same is true, however there's a unique output of a laser diode. Between two metallic surfaces is a semi-conductor that will output collimated light, or light who's rays are nearly parallel, and similar in wavelength.

See Laser diode - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Diode Pumped Solid State
Diode Pumped Solid State, or DPSS for short, is a way of getting stimulated emissions of radiation, through a conversion process. "Typical" red diode lasers will output 660nm of light directly from the diode as collimated light. With a DPSS laser, there are crystals that are "pumped" by a diode that doesn't have the same frequency as the outgoing light.

This is an example of where green lasers typically get their output from.
There's an 808nm pump diode, who's purpose is simply to push 808nm laser light into a Nd:YVO4 or Nd:YAG crystal which produces laser light at 1064nm.
In turn, directly after that, is another crystal (KTP) which is a frequency doubler, and will effectively double the frequency from 1064 to 532nm which is the green light we see at the out-put end of lasers.
See Diode-pumped solid-state laser - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Divergence
Divergence is a measure of how much a beam will spread over time. A lower divergence means that a laser will maintain it's "beam" longer, where a higher divergence will spread out more. This isn't to be confused with focus however. A laser that is focused to infinity will still have divergence.
To calculate divergence, please see pseudonomen137's mRad calculator here:
pseudonomen137's JScript mRad Calculator
See Beam divergence - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Driver
A Driver in laser terms is a circuit board that is designed to provide a laser diode with a filtered/consistent amount of power. Similar to a driver circuit, however is typically a series of resistors, circuits and other elements that convert raw output from a battery to a steady flow of electricity the diode can handle.
See Sam's Laser FAQ - Diode Laser Power Supplies for more information.
Flexdrive
A Flexdrive is a driver (see above) model, and is a trademarked design for specific electronic circuit by DrLava:
Micro Flex Drive
Adjustable or fixed drivers are reffered to as their type. (Fixed driver outputs a fixed mAh, adjustable can be changed)
Host
In laser terms, a host is simply the shell or casing/housing of a laser diode+driver+battery assembly. There are several styles of host that exist, from pen hosts, to torch hosts.
Infrared
Infrared is simply light that exists outside of the visible spectrum for our human eyes. It's been broken up into 3 categories:
IR-A: 700 nm–1400 nm
IR-B: 1400 nm-3000nm
IR-C: 3000 nm-1mm
Typically handheld/Diode lasers will be between 700nm and 1000nm, 980nm and 808nm being pretty common. 808nm is also the diode used for powering green lasers.
See Infrared - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
IR Filter
IR Filter, or Infrared filter is a filter that has been designed to block infrared frequencies. This is common in green lasers, because of the 808nm and 1064nm light that is produced in the conversion process into 532nm. It's also often noted that a lot of cheaper "Chinese lasers" are missing these, causing them to potentially be more dangerous.
See Infrared cut-off filter - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
KTP Crystals- Potassium Trihydrogen Phosphate This material is a nonlinear optical material which is used in the frequency doubling stage of DPSS green lasers, and is the final stage of the conversion process into 532nm wavelengths.
See Potassium titanyl phosphate - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Milliwatt (mw)
Milliwatt, or mw for short, is a measure of output of electricity, where one milliwatt is equal to one thousandth of a watt.
<5 mw lasers are referred to as the 'safe lasers' because the BAR (Blink Aversion Reflex) is fast enough to prevent damage to the retina, according to the FDA.
See Watt - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information on watts, and
See Corneal reflex - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information on Corneal or aversion reflex.
Module
With reference to a laser module, this is a component usually includes the diode housing, driver, KTP and YAG crystals in the case of a DPSS Green laser, collimating lens, widening lens, etc.

This is an example of what a laser module looks like.
Often for DIY or Do-it-yourself projects, these modules will be purchased separately from a host, for users who wish to customize their laser assemblies.
mRad
mRad stands for milliRad which is a unit of angular measurement. Usually used in the context of divergence, it's a way of measuring or describing how much a beam will spread out over time.
See: Radian - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Multifunction
Multifunction lasers are lasers that serve multiple functions. Such as being a laser and a flashlight.
Over-spec
Over-spec is shortened for "Over Specification". When purchasing a laser, the laser is going to be "spec'd" or given specifications, usually referring to the wattage or milliwatts. A laser which performs with a higher output compared to the listed specifications is often refereed to as being over-spec.
Pointer
A pointer, not to be confused for a torch, is usually referencing it's host, or intended meaning. The terms seem to be interchangeable.
See Laser pointer - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Pump
Pump refers to the role a diode plays in a DPSS laser. The pump is simply the source which goes through a conversion process before being released as a final product.
Alternatively, laser pumping is the act of transferring energy from an external source into the gain medium of a laser. (The element that lases)
See Laser pumping - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
TEM (Hermite-Gaussian Modes)
This refers to the output of the laser and "how it looks". Sometimes mode jumping occurs with lasers, and that's honestly all I know about it.
What I can tell you is that there's a little diagram that shows you what the different TEM's look like:

See Gaussian beam - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Thermal Paste
This is a paste that separates spaces between two surfaces, and helps conduct heat. If you look at a heat syncs surface and another surface that the heatsink sits on, there's usually microscopic gaps because the surfaces aren't actually flat.

This is an exaggerated view, however does represent what microscopic imperfections could/do look like.
By filling the "TIM" whitespace, you're allowing more heat to be conducted between the two surfaces. In this example, it's talking about a heatsink and CPU, but in laser terms it is typically the diode housing and the host or heatsink.
Torch
This is in reference to the type of host, as well as it's role. Torches are not typically "pointers" in that they're not often used for pointing at objects, though they have been known to be used for such activities.

This is an example of a host that is a torch style.
Under-spec
Opposite of Over-spec. Short for Under Specification.
Wavelength
Wavelength is the length at which a waves shape repeats.
To humans, different electromagnetic wavelengths represent different colors, and serve different functions.

This is an example of the electromagnetic spectrum, which includes the visual spectrum of what humans can see/perceive with their eyes.

This is a chart showing the frequency response most sensitive to humans. Notice that green is the most sensitive, meaning it'll be the "most bright"
See Wavelength - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
YAG-Yttrium Aluminum Garnet
Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (YAG for short) is a synthetic crystalline material used in solid-state lasers, and can be doped into YAG to create Nd:YAG lasers.
This is also the first stage of transformation in DPSS Green lasers.
See Yttrium aluminium garnet - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia for more information.
Last edited:



