Welcome to Laser Pointer Forums - discuss green laser pointers, blue laser pointers, and all types of lasers
Buy Site Supporter Role (remove some ads) | LPF Donations
Links below open in new window
FrozenGate by Avery
Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
More options

You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
A New Styropyro vid. Giant IR Laser.
- Thread starter steve001
- Start date


- Joined
- Oct 14, 2012
- Messages
- 6,086
- Points
- 113
Steve, thanks for sharing Styro's video with us!
You can never have too many "Death Ray" lasers. ☠
You can never have too many "Death Ray" lasers. ☠
- Joined
- Jul 10, 2015
- Messages
- 9,964
- Points
- 113
You know I posted this the 2 days ago
HERE > https://laserpointerforums.com/threads/videos-from-youtube-you-wish-to-share.98227/post-1557234
HERE > https://laserpointerforums.com/threads/videos-from-youtube-you-wish-to-share.98227/post-1557234
No I did not. And neither did bowtieguy. It seems if you post in someone else's thread your post does not show under "New posts" For that matter your reply did not show by the bell icon.You know I posted this the 2 days ago
HERE > https://laserpointerforums.com/threads/videos-from-youtube-you-wish-to-share.98227/post-1557234
Last edited:
Alaskan
0
- Joined
- Jan 29, 2014
- Messages
- 12,025
- Points
- 113
Yea, if you don’t search the forum for the video before posting, you won’t know it has been posted here before. I learned that one the same way.
Styro may have properly stated “shortwave IR” on this video, relative to longer WL IR, but it’s a bit misleading to call it that in a video meant to draw the attention of just anyone on the net, some might assume the wavelength is shorter than visible, he said that twice before I stopped watching.
Perhaps I’m just splitting hairs! But when he said that I assumed he misspoke for a bit, but he didn’t. Then realizing that, I had to go see how long is considered short:
Short-wave infrared (SWIR) light is typically defined as light in the 0.9 – 1.7μm wavelength range, but can also be classified from 0.7 – 2.5μm.
Styro may have properly stated “shortwave IR” on this video, relative to longer WL IR, but it’s a bit misleading to call it that in a video meant to draw the attention of just anyone on the net, some might assume the wavelength is shorter than visible, he said that twice before I stopped watching.
Perhaps I’m just splitting hairs! But when he said that I assumed he misspoke for a bit, but he didn’t. Then realizing that, I had to go see how long is considered short:
Short-wave infrared (SWIR) light is typically defined as light in the 0.9 – 1.7μm wavelength range, but can also be classified from 0.7 – 2.5μm.
Last edited:
- Joined
- Jul 10, 2015
- Messages
- 9,964
- Points
- 113
Steve, thanks for sharing Styro's video with us!
You can never have too many "Death Ray" lasers. ☠
That would be cool but it's not much of a " death ray " Now an active fiber laser a couple - few magnitudes stronger would be interesting.
It is neat to see him get a rough beam from that LIMO, I almost bought one a lot like it but they are really meant as pumps as they contain many emitters coupled to fiber.
Speaking of active fiber I wonder if the inner core of an active fiber laser could be doped so as to directly lase in a visible wavelength rather than pumping a crystal to make a high quality visible beam as active fiber can produce a very high quality beam
.......... if you post in someone else's thread your post does not show under "New posts" .............
Actually that is my thread.......
Styro may have properly stated “shortwave IR” on this video, relative to longer WL IR, but it’s a bit misleading to call it that in a video meant to draw the attention of just anyone on the net, some might assume the wavelength is shorter than visible, he said that twice before I stopped watching.
Perhaps I’m just splitting hairs! But when he said that I assumed he misspoke for a bit, but he didn’t. Then realizing that, I had to go see how long is considered short:
Short-wave infrared (SWIR) light is typically defined as light in the 0.9 – 1.7μm wavelength range, but can also be classified from 0.7 – 2.5μm.
Yes I used to mix up NEAR IR with SHORT IR.....oh wait, they are both listed as 700nm - 2500nm ( 0.7um - 2.5um )all over the web, but images like this make the two terms appear to be different. Here Near IR looks like 700nm - 1000nm and Short wave IR looks like 1000nm - 2500nm then medium wave and long wave.


What is SWIR?
Have a question about short-wave infrared (SWIR)? Find definitions, application uses, and examples at Edmund Optics.
www.edmundoptics.com
Last edited:
Alaskan
0
- Joined
- Jan 29, 2014
- Messages
- 12,025
- Points
- 113
I prefer to call it Near-IR, but whatever, far shorter than what a CO2 laser will produce.
- Joined
- Jul 10, 2015
- Messages
- 9,964
- Points
- 113
I prefer to call it Near-IR, but whatever, far shorter than what a CO2 laser will produce.
Yes CO2 is around 10400nm ( 10.4um ) but what I want is to know the real definition of the terminology so I can say it right, there is a lot of information online that's lacking, even Wikipedia and webesters just say 0.7-2.5um for either term, but I know I have heard people make a distinction, I just want to know the difference so I can get it right., I'm not being critical of anyone.
It looks like NIR is 0.7-1.0um and SWIR is 1.0-2.5um
---edit---
Correction :
CO2 lasers typically emit at a wavelength of 10.6 μm, but there are other lines in the region of 9–11 μm (particularly at 9.6 μm).

CO_2 lasers
CO₂ lasers are powerful infrared lasers using a gas mixture with carbon dioxide molecules being excited in a discharge.
Last edited:
Alaskan
0
- Joined
- Jan 29, 2014
- Messages
- 12,025
- Points
- 113
I agree with how you understand NIR, calling .7 to 1 um SWIR doesn't appear correct to me. However, if you google NIR, different sources have different views. I like this site: https://www.rp-photonics.com/infrared_light.html (but they show a portion of what I consider NIR, to be IR-A, up to 1400 nm).
Different definitions are used for distinguishing different infrared spectral regions:
The near-infrared spectral region (also called IR-A) ranges from ≈ 700 to 1400 nm. Lasers emitting in this wavelength region are particularly hazardous for the eye, as near-infrared light is transmitted and focused to the sensitive retina in the same way as visible light, while not triggering the protective blink reflex. Adequate eye protection is then very important.
- The short-wavelength infrared (SWIR, IR-B) extends from 1.4 to 3 μm. This region is relatively eye-safe, since such light is absorbed in the eye before it can reach the retina. Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers for optical fiber communications, for example, operate in that region.
- The mid-infrared (mid-wavelength infrared, MWIR, IR-C) ranges from 3 to 8 μm. The atmosphere exhibits strong absorption in parts of that region; there are many absorption lines e.g. of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). Many gases exhibit strong and characteristic mid-IR absorption lines, which makes this spectral region interesting for highly sensitive trace gas spectroscopy.
- The long-wavelength infrared (LWIR, IR-C) ranges from 8 to 15 μm, followed by the far infrared (FIR), which ranges to 1 mm and is sometimes understood to start at 8 μm already. This spectral region is used for thermal imaging.
Last edited:
- Joined
- Sep 12, 2007
- Messages
- 9,399
- Points
- 113
Yes CO2 is around 10400nm ( 10.4um )
"the principal wavelength bands centering on 9.4 and 10.6 micrometers (μm)."
- Joined
- Jul 10, 2015
- Messages
- 9,964
- Points
- 113
Thanks for the 411 Cyparagon, still learning all the time. 
Arctos
Member
- Joined
- Mar 6, 2019
- Messages
- 39
- Points
- 8
Speaking of active fiber I wonder if the inner core of an active fiber laser could be doped so as to directly lase in a visible wavelength rather than pumping a crystal to make a high quality visible beam as active fiber can produce a very high quality beam
Yes it can be done but not at particularly high powers in visible range yet.. Few watts max typically. Been waiting a long time for that to increase over time. All the high power stuff so far I've seen and worked with is fibre pumped bulk laser though.
Below is an er doped ZBLAN fibre laser showing various emission spectra it can handle.
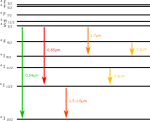
Fiber Laser - FiberLabs Inc.
Introduction Fiber lasers are one class of solid-state lasers in which the gain medium is an optical fiber. Fiber lasers have been a key technology in the area of solid-state lasers, since the first proposal of using an optical fiber as a mode selector for lasers . An example of basic fiber...
One unusual advantage that can occur from cladding pumping like this is tolerating high back reflections with a cladding stripper/mode stripper. Very hard for the light to get out of the SM fibre to the MM cladding. One issue for frequency conversion is the broadband output of many fibre lasers.. have fun


